
Transcranial Doppler is used to identify and interrogate the intracerebral arterial system. Normally the skull is impenetrable to Ultrasound waves, but using certain windows allows adequate penetration to monitor cerebrovascular hemodynamics.
Indications
- Sickle Cell Disease Stroke prevention monitoring
- Detection of Vasospasm post Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
- As an adjunct to diagnose brain death
- Assessment of increased intracranial pressure
Parameters
- Resistive Index – Resistance to blood flow caused by microvascular bed distal to the site of measurement.
- TAMx – The time mean of the peak velocity envelope, the envelope being a trace of the peak velocity as a function of time
- Peak Systolic Velocity (PSV) – The maximum value of flow velocity in systole, at the apex of the waveform
- End Systolic Velocity (EDV) – The velocity measured at end diastole, usually at the lowest point before a new waveform begins
Anatomy


The vessels that comprise the intracranial arteries arise from the Aortic arch. There are 3 vessels in the Aortic arch the Brachiocephalic (aka Innominate), the Left Common Carotid artery and the Left Subclavian artery. The Vertebral artery (VA) is a branch of the Subclavian arteries The common carotid arteries bifurcate into Internal and External carotid (ICA and ECA). The ICA courses cephalad and pierces the cranium to enter the brain. The ICA has several segments:
- Cervical Extends from the bifurcation
- Petrous Courses through the petrous portion of the temporal bone.
- Cavernous Parasellar portion, the siphon gives rise to first major branch OA
- Cerebral/Supraclinoid Terminates in MCA/ACA bifurcation

Once the ICA enters the brain it gives off the Opthalmic artery, Posterior communicating artery and Terminates in the Anterior and Middle cerebral artery bifurcation.
Circle of Willis

Named eponymously after Thomas Willis, the Circle of Willis is an anastomotic vascular ring at the base of the brain. It is made up of the ACA, PCA, Posterior communicating (PcomA) Artery and Anterior communicating Artery (AcomA).




Scanning
The technique involves using several windows.
Temporal

In the temporal window you will scan the MCA, ACA and PCA advancing 2mm from distal to proximal in the MCA. Using a zero degree angle and a moderate sized gate. Flow directions are as follows. In the temporal window angling down you will be able to insonate the terminal ICA

MCA – Above baseline (typically highest in velocity)
ACA – Below baseline
PCA – Bi-directional (lowest in velocity of the 3 vessels)
Occipital/Trans-Foraminal
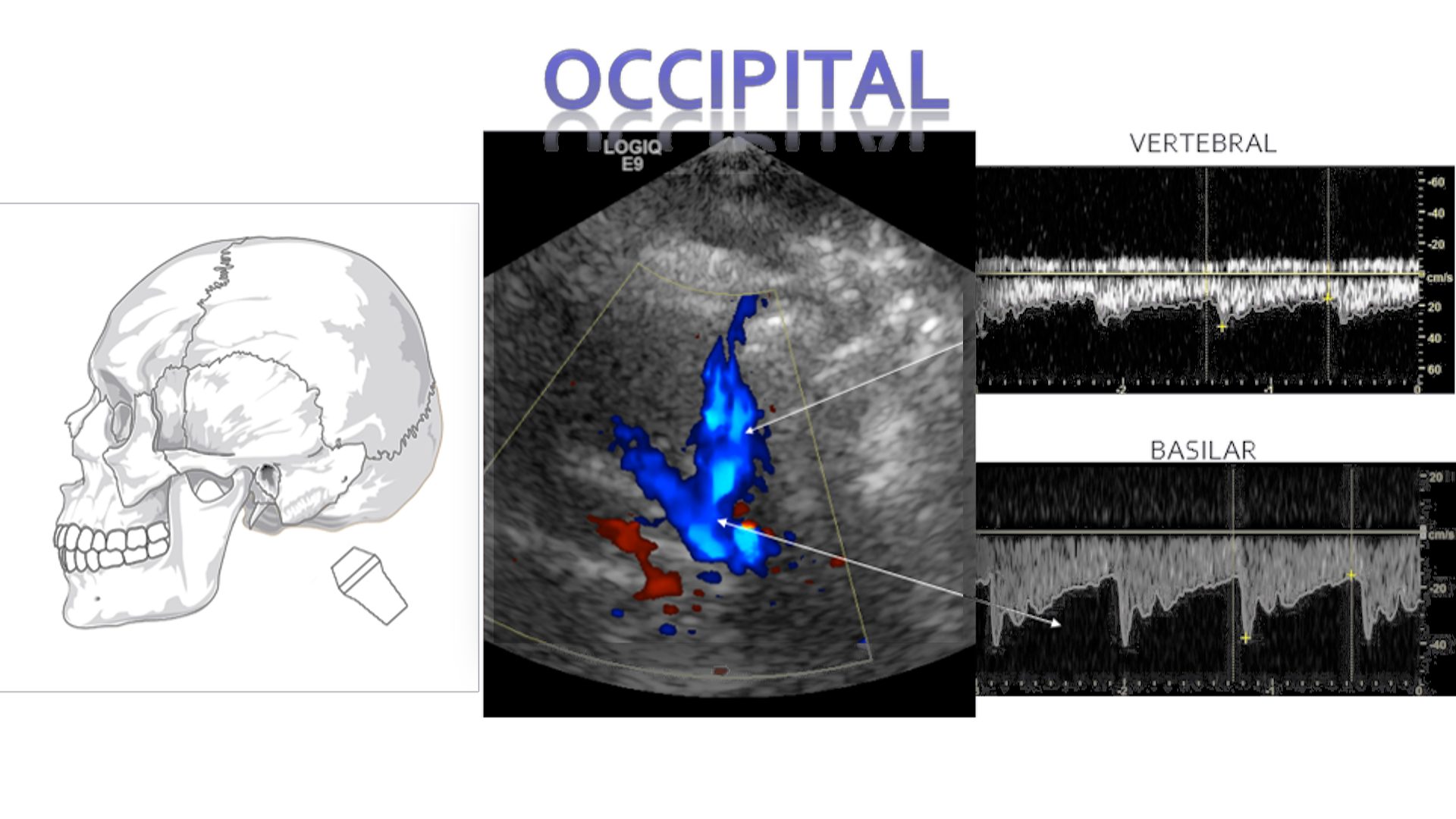
In the occipital or trans-forminal window you will encounter the bilateral Vertebral arteries and singular Basilar artery. The flow will be below baseline for both. These arteries join to form the posterior cerebral arteries.
Orbital

In this window you will be able to scan the OA. Use a small amount of sterile gel rubbing it onto the transducer face to make a thin film. You can also use a tegaderm patch over the eye to make a barrier for scanning.
Normal Values
Adult:

Advances in Transcranial Doppler US: Imaging Ahead Jonathan D. Kirsch, et. al. RadioGraphics 2013; 33:E1–E14
Pediatric:

Sickle Cell Criteria

A-9-year-old-child-with-Sickle Cell Disease a TCD-demonstrates-abnormal-right MCA time-average. (a)TCD shows elevated MCA velocities. (b) CT angio shows narrowing of the proximal MCA andACA.

16 yo F with SCD showing elevated PSV in the LT ACA and RT MCA. On MR Angio she was found to have stenoses at both these sites.
19 yo F in Sickle Cell crisis in the ICU. TCD shows reduced velocities bilaterally. Patient later died from many complications of sickle cell disease.

____________________________________________________________________________________________
Vasospasm Criteria

8 month old F fall that caused a Subarachnoid Hemmorhage. Serial TCD’s show progression of vasospasm.

Brain Death

Defined as the complete and irreversible cessation of brain function due to a total arrest of cerebral blood flow. The three essential findings in brain death are coma, absence of brainstem reflexes, and apnea. Cerebrovascular arrest usually follows some catastrophic event as brain trauma and or hemorrhage or prolonged ischemia.
Brain death can be confirmed with ancillary tests such as Nuclear Medicine, EEG and TCD.
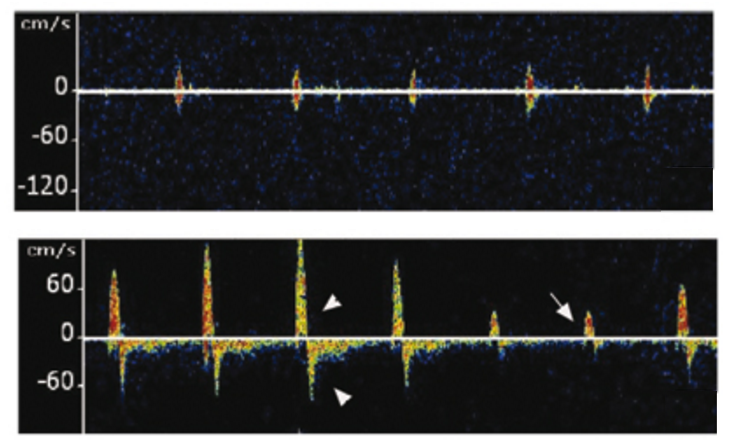
On TCD you’ll encounter doppler signals that have sharp systolic spikes and no diastolic flow. Later on reversal of flow occurs. 2 scans separated by 30 minutes should be performed.







Great post! You have a way of explaining things that makes them very easy to understand.
I visit your website fairly often and I’m always impressed.
Keep up the great work!
LikeLike
Thanks!
LikeLike
Hi Henry,
When calculating the Lindegaard Ratio, which ICA velocity do you use? Terminal or ICA in the neck?
Great post by the way! Thank you so much 🙂
LikeLike
Hey there thanks! We use the terminal ICA
LikeLike
Hi Henry,
I just happened to come across your work here and on YouTube and am really impressed. We might be featuring this lesson on our Facebook pages for Vascular-Web and Vascular Morning News. We know it will be well received and hope that it increases traffic to your website.
Keep up the excellent work!
Best regards,
Richard Keith H. Duncan
Pres/CEO Echo-Web/Vascular-Web
LikeLike
Greet Job.Thank you. Does TCD allows imaging evaluation of venous system such as IJV?
LikeLike
It is not part of the protocol to check Internal jugular veins for TCD analysis
LikeLike
Hi, thanks for the lecture.
What’s the difference between TA MAX and TA Mean in the machines. I use a logiq P6, a Vivid E9 and S6.
Thanks
LikeLike
Hi, thanks for the lecture.
What’s the difference between TA MAX and TA Mean in the machines. I use a logiq P6, a Vivid E9 and S6.
Thanks
LikeLike
Hi Henry,
what’s the difference between: time-averaged maximum velocity (TAMAX or TAP) and time-averaged mean velocity (TAMEAN) in the machines? I use a Vivid S6 or E9 and a Logiq P6.
Thanks
Letícia
LikeLike
Excelente, thanks
LikeLike
Excellent. Any form about to exchange information about cases?
LikeLike
Hey Yuri, you can message me on instagram for exchanging info on cases
LikeLike
Excelente! Muy práctica.. Felicitaciones
LikeLike
Henry, I’m very new to your YouTube videos. I get a lot of information from them and I’ve been doing vascular ultrasound for almost 30 years! Do you have any videos specifically regarding Duplex TCD for PFOs?
LikeLike